官方下载地址:https://gitlab-runner-downloads.s3.amazonaws.com/latest/index.html
官网安装文档:https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/install/linux-manually.html
sudo curl -L --output /usr/local/bin/gitlab-runner "https://gitlab-runner-downloads.s3.amazonaws.com/latest/binaries/gitlab-runner-linux-arm" sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/gitlab-runner #Create a GitLab CI user: sudo useradd --comment 'GitLab Runner' --create-home gitlab-runner --shell /bin/bash #Install and run as service: sudo gitlab-runner install --user=gitlab-runner --working-directory=/home/gitlab-runner sudo gitlab-runner start
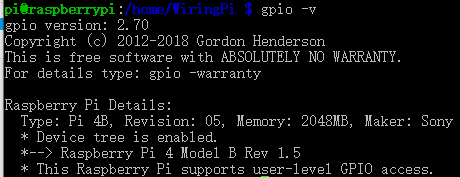
安装过程如下图所示:

设置gitlab-runner开机启动:
sudo systemctl enable gitlab-runner
如果出现跑cicd的时候有如下提示:

则需要使用vi编辑/home/gitlab-runner下的.bash_logout文件(这个文件用ls指令是看不到的),将里面的所有内容都注释掉后重新跑cicd即可: