测试环境服务器参数:
CPU:4核8G带宽200M
RDS:1核1G
操作系统:Linux
JDK版本:1.8
WEB容器:Tomcat 8
压测工具:JMeter 3.2
每个组合分别的test内容基本如下(根据搭配的数据库不同,有些方法命名稍有差异):
@Controller
@RequestMapping("")
public class RootController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@RequestMapping(value={"","/","/index"})
String view(Map<String, Object> map){
System.out.println("首页(default)");
map.put("name", "SpringBoot");
map.put("date", new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date()));
return "index.jsp";
}
@RequestMapping(value={"test1"})
@ResponseBody
String test() {
String str = "(new Random()).nextInt() = "+(new Random()).nextInt();
System.out.println(str);
return str;
}
@RequestMapping(value="test2")
public void test2(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
String str = "(new Random()).nextInt() = "+(new Random()).nextInt();
System.out.println(str);
ResponseStaticUtil.write(response, str);
}
@RequestMapping(value={"get1"})
@ResponseBody
String get1() {
User user = this.userService.get(1);
String str = "user = "+user.getName()+" / (new Random()).nextInt() = "+(new Random()).nextInt();
System.out.println(str);
return str;
}
@RequestMapping(value="get2")
public void get2(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
User user = this.userService.get(1);
String str = "user = "+user.getName()+" / (new Random()).nextInt() = "+(new Random()).nextInt();
System.out.println(str);
ResponseStaticUtil.write(response, str);
}
@RequestMapping(value={"list1"})
@ResponseBody
String list() {
List<User> users = this.userService.listAll();
String str = "users.size()= "+users.size()+" / (new Random()).nextInt() = "+(new Random()).nextInt();
System.out.println(str);
return str;
}
@RequestMapping(value="list2")
public void list2(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
List<User> users = this.userService.listAll();
String str = "users.size()= "+users.size()+" / (new Random()).nextInt() = "+(new Random()).nextInt();
System.out.println(str);
ResponseStaticUtil.write(response, str);
}
}
普通SpringMVC+Hibernate项目的各Controller压力测试结果:
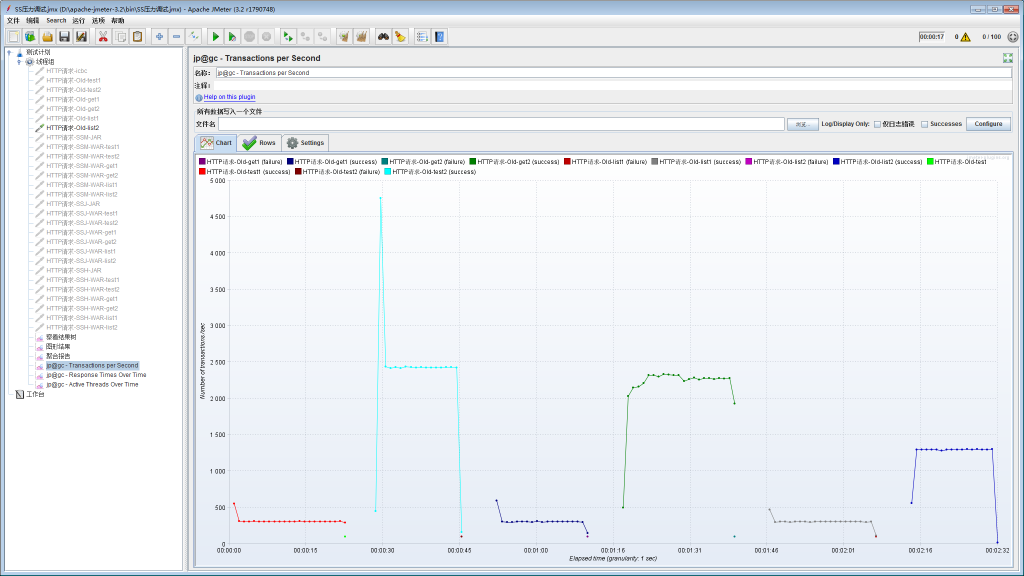
SpringBoot+MyBatis项目的各Controller压力测试结果:
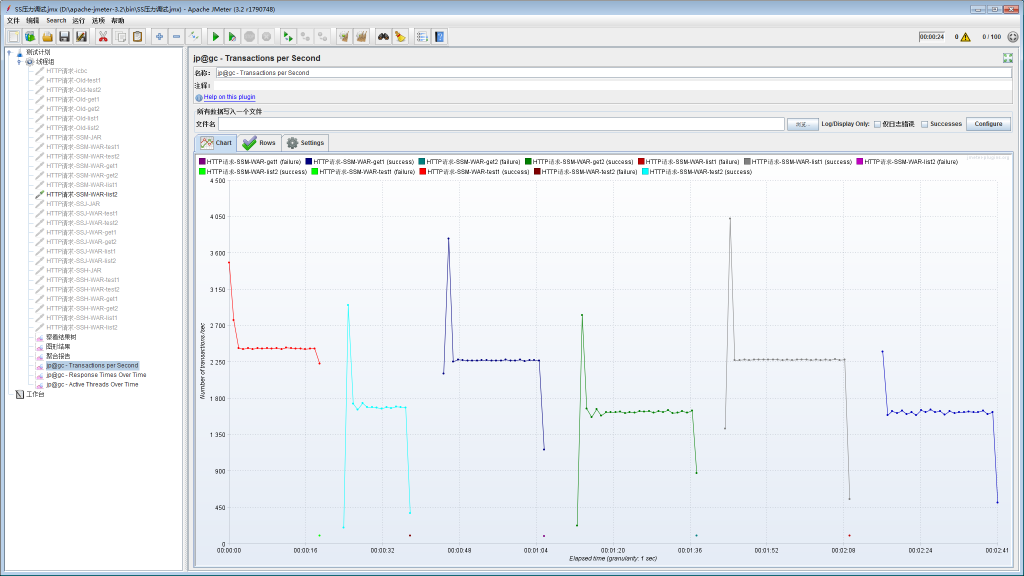
SpringBoot+JPA项目的各Controller压力测试结果:
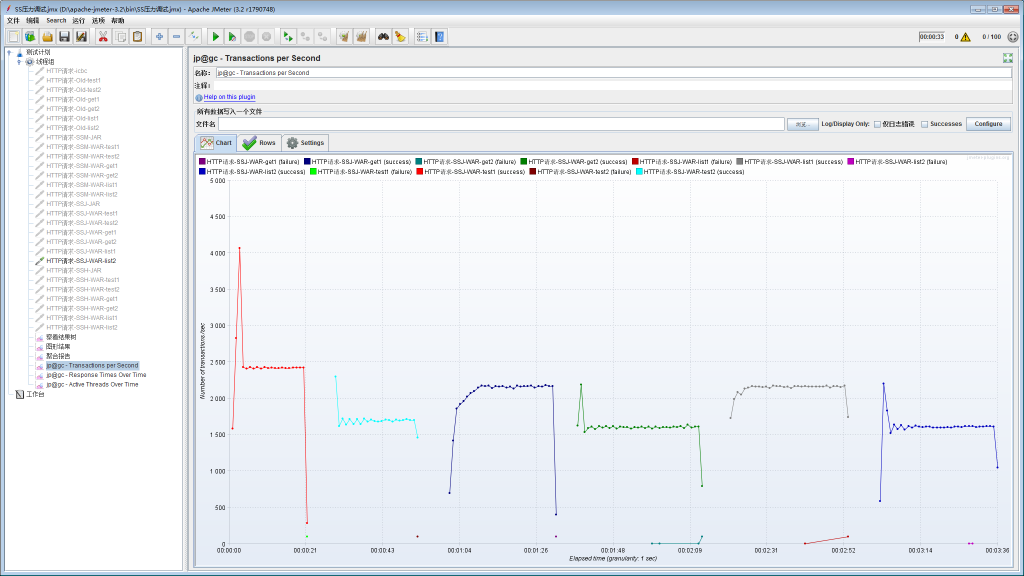
SpringBoot+Hibernate项目的各Controller压力测试结果:

” SpringBoot+MyBatis / SpringBoot+JPA / SpringBoot+Hibernate ” 的get单个user对象压力测试对比:

” SpringBoot+MyBatis / SpringBoot+JPA / SpringBoot+Hibernate ” 的获取user所有对象(只有3个数据)压力测试对比:
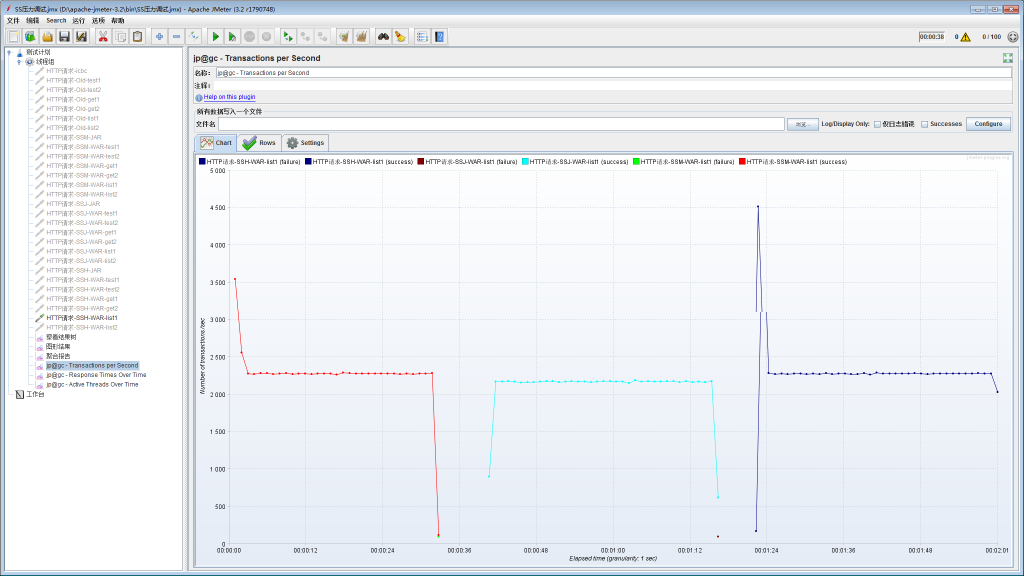
总结:
1、在写Controller方法时,普通SpringMVC框架在使用普通的response.write的方式时效率很高,但使用annotation的方式返回数据时效率十分低;反之,使用SpringBoot框架在使用annotation的方式返回数据时效率比传统的response.write方式的运行效率要高出一截。
2、在SpringBoot框架下搭配分别搭配MyBatis、JPA、Hibernate时,其运行效率的差异不大,JPA的方式稍弱一点点。
本文属于“cp锋”的原创,虽然内容不是十分精品,但还望尊重本人的研究成果,转发时请注明转载并带上本页面链接,感谢~